EXERCISE
A. Objective Questions
1. Write TRUE or
FALSE for each
statement.
a) The
molecules of each substance are identical. FALSE
b) The inner
molecular forces are effective at all distances between two molecules. FALSE
c) The
molecules in a substance are in random motion. TRUE
d) In a gas,
the molecules can move anywhere in space. TRUE
e) The
liquids are less viscous than the gasses. FALSE
2. Fill in the blanks
a) All the molecules of a substance are identical
b) The inter-molecular spacing is least in solids, more in liquids and
still more in gases.
c) The molecular motion in
liquid and gas is in zig-zag path.
d) In a solid the molecules vibrate on either side but
they remain at
their fixed position.
e) The inner molecular
forces are the weakest in gases.
f) A solid exerts pressure downwards on its base.
g) The gases are least
dense.
3. Select the
correct alternative.
a) The diameter of a
molecule is approximately
(i) 1 cm (ii)
10 cm
(iii)10 -10 cm (iv) 1m
b) The inner
molecular forces are stronger in
(i) Solids (ii) Liquids
(ii) Gases (iv) both (i) and (ii)
c) The molecules
(i) In solid,
liquid and gas move freely anywhere.
(ii) In a solid
move freely within its boundary.
(iii) In a liquid move within its
boundary.
(iv) In a gas
moves only within its boundary.
d) The solids are
(i) More dense (ii) less
dense
(iii) Least
dense (iv)
highly compressible
e) The inter-molecular forces in liquids are
(i) As strong
as in solids.
(ii) Stronger
than in solids.
(iii) Weaker than in solids.
(iv) Weaker
than in gases.
4. Match the
following columns.
Column A Column B
(a) A molecule is composed of (i)
does not exist free in nature
(b) Ice water and water vapour (ii) Can vibrate only up to
about 10 -10
m from their
mean positions
(c) An atom (iii)
atoms
(d) Gases (iv)
are the three states of
water
(e) The molecules of a solid (v) Occupy space
Ans. (a)-(iii),
(b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(v), (e)-(ii)
B. Short/Long answer
questions
1. Define
matter. What is its composition?
Matter is defined
as anything which occupies space and has mass.
It can be perceived
by our senses of smell, touch, sight, hearing
and taste. Some
examples of matter are Air, water, hydrogen,
oxygen, sugar,
sand, steel etc. Matter is composed of tiny particles
known as atoms.
2. Name the three states of matter.
The three states of
matter are solid, liquid and gas.
3. What is a molecule?
that is capable of independent existence. A
molecule is made
up of one or more
than one atoms of the same kind or of different kinds.
4. What is the approximate size of a molecule?
The approximate
size of a molecule is 10-9 m.
5. One litre of water has 6.02 x 1026
molecules. Estimate the size of a
molecule.
Volume of one litre water = 10-3 m3
One litre of water has 6.02 x 1026 molecules.
So volume of one water
molecule = 1.6 x 10-30 m3
4/3ℼr³ = 1.6 x
10-30 m3
So r = 0.725 x 10-10m
6. What do you mean by
inter-molecular spacing?
The spacing between the particles of a matter is known as intermolecular
spacing.
7. Describe a simple experiment to illustrate
the existence of intermolecular
spacing.
Take 100 ml of water in a measuring cylinder. Add 20gm of
salt in the
water gently and stir it well, so that the salt dissolves
well in the water.
You can notice that the level of water does not change even
after
adding the sugar. It shows that the particles of salt have
occupied the
spaces between the particles of water. Hence it is proves the
existence of intermolecular spacing.
8. What do you
mean by intermolecular forces?
The force of attraction
between the particles of a substance is known as
intermolecular force.
9. What
are the forces of cohesion and adhesion?
The force of attraction between the particles of same
substances is called the force of cohesion or cohesive force. Whereas the force
of attraction between the particles of different substances is called the force
of adhesion or adhesive force.
10.
State three characters of molecules of matter which determine its
solid, liquid and gaseous state.
The three characters of molecules which decide the state of a
matter
Are:
(i) Inter-molecular space
(ii) Force of attraction between the molecules.
(iii) Movement of molecules.
11.
State the approximate spacing between two molecules of a matter.
The approximate spacing between two molecules of a matter is
12. How
do solids, liquids and gases differ in their following properties?
(a) Size (b)
Shape (c) Density.
Properties
|
Solid
|
Liquid
|
Gases
|
Size
|
Definite
|
Definite
|
Indefinite
|
Shape
|
Definite
|
Acquires the shape
of the container
|
Acquires the shape
of the container
|
Density
|
High density
|
Low density
|
Negligible
|
13. The molecules in a substance are in motion. What type of
path do
they follow?
The molecules in a substance are in random motion and they
move
in a zig zag path.
14. Describe a simple experiment to illustrate that molecules
are not at
rest, but they constantly move.
When we observe the sunlight coming through a minute opening
in a
darkened room, the fine dust particles appear to dance in a
random
and zig zag manner. This is because the air particles
surrounding the
dust particles are in a random motion and they hit the dust
particles
causing to make them move in a zig zag path. This observation
concludes that molecules move constantly and are not in rest.
15.
Write down five general properties of solids, liquids and gases.
Properties
|
Solid
|
Liquid
|
Gases
|
Mass
|
Definite
|
Definite
|
Definite
|
Shape
|
Definite
|
Acquires the shape
of the container
|
Acquires the shape
of the container
|
Volume
|
Definite
|
Definite
|
Indefinite, acquires
the volume available
|
Compressibility
|
Not compressible
|
Negligibly
compressible
|
Highly compressible
|
Fluidity
|
Not possible
|
Can flow
|
Can flow
|
16. Give
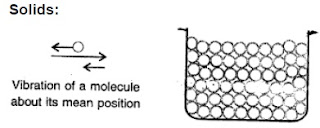
the molecular model for solid and use it to explain why a solid
has a definite volume and definite shape.
The molecules in a
solid are closely
packed. The
intermolecular force is
the strongest in solid
and the intermolecular
space is negligible. The molecules are arranged in a definite
manner, therefore solids have a definite shape.
The molecules of a solid do not leave their position. They
can only
vibrate on the either side of their mean positions. Therefore
solids
have definite volume or size.
17. Describe the molecular model for a liquid.
How does it explain that a
liquid
has no definite shape, but has a definite volume.
The
inter-molecular
force in
liquid is not as
strong as it
is in solids. So
the molecules
in liquids
are loosely
packed
and are not
fixed. The
molecules can
move
only within
the boundary of the liquid. That is why a liquid has a
definite
volume, but no definite shape. Liquid takes the shape of the
container in
which it is placed.
18. A gas has neither a definite volume nor a
definite shape. Describe the
molecular model to explain it.
The molecules of a gas lie much farther apart than they lie
in solids or
liquids. The inter-molecular force is negligible, so the
molecules are free
to move in the entire space
available to them. They
move in all possible
directions at all possible
speed. Thus a gas has
neither a definite volume
nor a definite shape.
19.
Distinguish between the three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas
on the basis of their molecular models.
Solid
|
Liquid
|
Gas
|
The molecules
in a solid are closely packed.
|
The molecules
in a liquid are loosely packed.
|
The molecules
in a gas are wide apart.
|
The
inter-molecular force in solid is very strong.
|
The
inter-molecular force in liquid is less strong.
|
The
inter-molecular force in gas is very weak.
|
The molecules
in solid are fixed at their position. They can only vibrate about their mean
position.
|
The molecules
in a liquid can move within the boundary of the liquid.
|
|
The molecules
in a solid are closely packed, therefore solids are highly rigid and they
have high density.
|
The molecules
in a liquid are less closely packed,therefore liquids are less rigid and they
have low density.
|
The molecules
in a gas are wide apart, therefore gases are not rigid and they have least
density.
|
20.
Distinguish between solids, liquids and gases on the basis of their
following properties:
(a) Compressibility (b) Fluidity
(c) Rigidity (d) Expansion on
heating
Properties
|
Solids
|
Liquids
|
Gases
|
Compressibility
|
Not compressible
|
Negligibly compressible
|
Highly compressible
|
Fluidity
|
Not possible
|
Can flow
|
Can flow
|
Rigidity
|
Highly rigid
|
Less rigid
|
Not rigid
|
Expansion on heating
|
Low
|
More than solids
|
More than liquids
|
21. What
do you mean by change of state of matter? Explain:
(a) The change of a solid into a liquid at a
constant temperature, and
(b) The change of a liquid into a gas at a
constant temperature.
The change of state of matter of a substance from solid to
liquid or
from liquid to solid is done by imparting heat energy to it
at a constant
temperature.
(a) The process of change of a substance from the solid state
to its
liquid state on absorption of heat at a particular
temperature called
the melting point, is known as melting or fusion
(b)
The process of change of a substance from liquid state to its
gaseous
state at a particular temperature called the boiling point, is
known
as boiling or vaporization.
********************************************************************
Extra
Questions and Answers
A. Objective Questions
1. Fill in the
blanks
(a) Matter is a substance
that occupies space and has mass
(b) A molecule is
the smallest particle that can exist freely in nature.
(c) The molecules are
separated from each other with spaces called
intermolecular space.
(d) The force of attraction
acting between the molecules is called
Intermolecular force.
(e) In gas the
molecules are not rigid.
(f) The melting point of ice is 00 C
(g) Boiling point of water
is 1000
C
(h) A molecule or a cluster
of several molecules is called a nanoparticle.
(i) Plasma is the fourth state of
matter.
(j) Ancient Indian philosophers considered that
all kind of matter is made
up of five elements.
2. Correct the following statements.
(a) Greek thinker John Dalton called the smallest particle of matter as
atom.
Greek thinker Democritus
called the smallest particle of matter as
atom.
(b) Matter is composed of
very tiny particles known as molecules.
Matter is composed of very tiny particles
known as atoms.
***************************************************************************
(c) Atom is the simplest and smallest particle of a
substance that is
capable of
independent existence.
Molecule is the simplest and
smallest particle of a substance that is
capable of
independent existence.
(d) A molecule having more than two atoms is called a diatomic
molecule.
A molecule
having more than two atoms is called a polyatomic
molecule.
(e) Gas has a low thermal expansion. It expands a
little on heating.
Solid has a low thermal expansion.
It expands a little on heating.
(f) A liquid
exerts pressure on the walls of its container.
A gas
exerts pressure on the walls of its container.
(g) A liquid exerts pressure on its base downward.
A liquid
exerts pressure in all directions.
(h) The process of
change of a substance from liquid state to its gaseous
state is called melting.
The process of change of a substance from
liquid state to its gaseous
state is called boiling or vaporization.
(i) Solids have only one free surface.
Solids have any number of free surface.
(j) Solids are negligibly compressible.
Solid are not compressible.
3. Select the
correct alternative.
a) A small drop of
water contains about ____ particles of water in it.
(i) 1020 (ii) 1021 (iii) 1010 (iv) 1022
b) The diameter of
water molecule is
(i) 1.45 x 10-19 m (ii) 1.45 x 10-9
(iii) 1.45 x 10-10 m (iv) 1.45 x 10-20 m
c) One kg of
hydrogen contains _________ particles of hydrogen in it.
(i) 1.62 x 1026 (ii)
1.26 x 1026
(iii) 6.20 x 1026 (iv) 6.02 x 1026
d) Which of the
following are mono-atomic molecules
(i) Neon and argon (ii) hydrogen, oxygen
(iii) water,
ammonia (iv) none of these
e) A gas exerts pressure
(i) On the wall of its container
from all direction.
(ii) in all directions
(iii) on its base.
(iv) All of the above.
f) Liquids are
(i) Highly rigid (ii) Less rigid (iii) not
rigid (iv) none
g) Viscosity in gas
is
(i) less than liquid
(ii)
More than liquid
(iii) More than solid
(iv) Equal to solid
B. Short Questions and Answers
1. Define Matter. What is it’s composition?
Matter is defined as anything which occupies space and has mass.
It can be perceived by our senses of smell, touch,
sight, hearing and
taste.
Matter is
composed of tiny particle known as atoms.
2. What do you mean by Panchatatvas?
Ancient Indian Philosophers
considered that all kind of matters are
made up of five elements (
tatvas). These are Sky (akash), Air (Vayu),
Fire (Tejas),
Water (ap) and Earth
(prithivi). These are called as
panchatatvas
3. What is monoatomic molecules? Give
examples.
A molecule consisting of only one
atom is called monoatomic molecule.
Neon and Argon are examples of monoatomic molecules.
A molecule having two atoms is
called diatomic molecule. Hydrogen
and Oxygen are examples of diatomic
molecule.
5. What is polyatomic molecule? Give
examples.
A molecule having more than two
atoms is called polyatomic molecule.
Water and Ammonia are examples of polyatomic molecule.
1. What was Maharishi Kannada’s opinion on the composition of matter?
6. Define the followings.
(i) Solid state
When the intermolecular force is very strong,the
intermolecular space
is negligible and the molecules are not free to move, matter
exists as
solid.
(ii) Liquid state
When the intermolecular force is weak, intermolecular space
is more
as compared to solids and the molecules are free to move to
and fro
whithin a limited space, matter exists as liquid.
(iii) Gaseous state
When the intermolecular force is very weak or negligible,
intermolecular space is far more than the liquids and the
molecules
are free to and fro anywhere, matter exist as gas.
(iv) Melting or fusion
The process of change of a substance from the solid state to
liquid
state on absorption of heat at a particular temperature
called its
melting point is known as melting or fusion.
(v) Boiling or vaporisation
The process of change of a substance from the liquid state to
its
gaseous state at a particular temperature called its boiling
point is
known as boiling or vaporisation.
7. Give reasons
(i) It is easy to move the hand through water
but difficult to move the
hand in glycerine.
The intermolecular force of attraction is more in glycerine
than water. So
It is easy to move the hand through water but difficult to
move the
hand in glycerine.
(ii) It is easy to break a piece of chalk but
difficult to break a piece of coal.
The intermolecular force of attraction in chalk is less than
in coal. So it is
Easy to break a piece of chalk but difficult to break a piece
of coal.
(iii) It is easy to move a body in air than in
water.
It is easy to move a body in air than in water because the
force of
attraction between the air particles is very small and thus
the distance
between them is more as compared to that between air
particles.
(iv) Solids cannot be compressed much
The intermolecular force in solids is very strong. The
molecules in a solid
are closely packed and the intermolecular space is negligible.
Therefore solids cannot be compressed much.
C. Long Questions and Answers
1. What was Maharishi Kannada’s opinion on the composition of matter?
Maharishi Kannada was an Indian
Philosopher and the first person who
as anu and each anu
is made up of still smaller particles called Parmanu .
2. Who was John Dalton
and what was his finding about matter?
John Dalton was an English
chemist. From his experiment he found that
every matter is made up of molecules. A molecule is made up
of one or
more than one atom of the same
kind or of different kinds. A molecule
can exist free in nature. It is
the simplest and smallest particle of a
substance that is capable of independent
existence.
3. What are the
characteristics of particles of matter?
The particles of matter called
molecules have the following four
characteristics.
(i) They are very small in size.
(ii) They have spaces between them.
(iii) They are in constant random
motion.
(iv) They always attract each
other.
4. What are the properties of solids?
The properties of solids are
(i) A solid has a definite shape and size.
(ii) A solid can not be compressed.
(iii) The molecules in a solid are very closely packed.
(iv) A solid has very strong intermolecular force of attraction.
(v) In a solid the molecules are not free to move from their
positions.
They simply
vibrate on either side of their mean position.
(vi) A solid can have any number of free surface.
(vii) A solid is highly rigid.
5. What are the properties of liquids?
The properties of liquids are
(i) Liquids have a definite volume, but no definite shape.
They acquire
the shape of the
container in which they are kept.
(ii) Liquids are negligibly compressible.
(iii) The molecules in a liquid are loosely packed.
(iv) A liquid has weaker intermolecular force than solids
(v) The molecules in a liquid are free to move within the
boundary of the
liquid.
(vi) Liquids have only one free surface.
(vii) Liquids are less rigid.
6. What are the properties of gas?
The properties of gas are
(i) A gas has neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
It acquires
the shape and
volume of its container.
(ii) Gases are highly compressible.
(iii) In gas the molecules are least closely packed.
(iv) In gas there is no force of attraction between its
molecules.
(v) In gas, the molecules are free to move in a random manner
in
zig-zag paths
everywhere.
(vi) A gas has no free surface.
(vii) Gases are not rigid.



Comments
Post a Comment