EXERCISE
Multiple
Choice questions:
1.
Tick (√)
the appropriate answer.
(i) Identify the plant which has compound leaves.
(a) Banana (b) Banyan
(c) Mango (d) Rose
(ii) Which one of the following is not an insectivorous plant?
(a) Pitcher plant (b) Venus flytrap
(c) Bladderwort (d) Cactus
(iii) This leaf shows parallel venation.
(a) Banana (b) Mango
(c) Banyan (d) Guava
(iv) The point on the stem from where the leaf arises is
(a) Petiole (b) Lamina
(c) Node (d) Trunk
(v) Which one of the following is essential for photosynthesis?
(a) Carbon
dioxide (b) Nitrogen
(c) Oxygen (d) Soil
Short
Answer questions
1.
Name the following
(i) The part of the plant which grows under the ground: Root system
(ii) The part of the plant which grows above the soil: Shoot system
(iii) The wide flat portion of the leaf: Lamina
2.
What are the four functions of roots?
a) Root fixes the
plant in soil.
b) It absorbs
water and minerals from soil for the growth of entire plant.
c) It binds the
soil together and helps in soil conservation.
d) Some modified
roots store foods. i.e, Radish and Carrot.
3.
Mention the functions of the following:
i)
Spines
Spines are
modified leaves, which help to reduce water loss
ii)
Tendril
In case of certain weak stemmed plants, the leaves or
leaflets are modified
in to wiry, coiled structures. These are called
tendrils. They are sensitive to
touch. As they touch any object they coil around it
and support the plant to
climb up. Example: Sweet pea.
iii)
Scale leaves
Some plants like onion, ginger have thin and dry or
thick and fleshy scale
leaves. Their function is to protect the buds.
4.
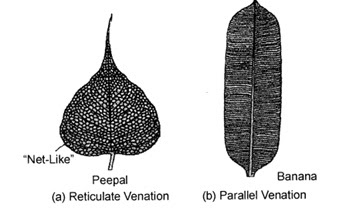
Define venation. What are the different types of venation found in leaves?
Arrangement of veins in a lamina is called venation.
They are mainly of
Two types.
Reticulate venation: In this type venation, veins and veinlets
are irregularly
distributed in the lamina and forms a network. e.g,
dicot plants like Peepal,
mango and guava
Parallel venation: In this type venation veins run parallel to
each other.
e.g, monocot plants like banana, grass, maize and
wheat leaves.
5.
Describe the modification of leaves in any one insectivorous plant.
The leaves of Venus flytrap plant have long hair. It
is divided in to two
parts having a midrib in between like a hinge. When an
insect visits the
leaf, it closes its two parts and trap the insect. The
insect then digested
by the digestive juice secreted by the leaf.
6.
Write the two main functions of leaves.
The two main
functions of leaf are photosynthesis and transpiration.
7.
Define: (i) Photosynthesis (ii)
Transpiration.
(i) Photosynthesis:
The process by which a plant leaf prepares or
synthesizes food from water and carbon dioxide in the
presence of
chlorophyll and sunlight is called photosynthesis.
(ii) Transpiration:
This is the process by which water is lost in the form of
water vapour by evaporation from the surface of leaves
and other
aerial parts of a plant. It has a cooling effect and
it develops a
suction force to make the roots absorb more water and
minerals
from soil.
Long
answer questions:
1. Giving example differentiate between the following.
(i) Tap root and fibrous root (ii) Simple leaf and compound leaf
(iii) Parallel venation and reticulate
venation.
(i) Tap root and
fibrous root
Tap root
|
Fibrous root
|
Tap root system
has a thick main root called primary root and many side branches called
secondary root.
|
Fibrous root
system has a cluster of roots of the same thickness.
|
Tap root system
found in dicot plants
|
Fibrous root
system found in monocot plants.
|
Ex.- Plants such
as gram, pea etc.
|
Ex.- Plants such
as maize, grass, banana etc.
|
(ii) Simple leaf
and compound leaf
Simple leaf
|
Compound leaf
|
In a simple leaf
the lamina is undivided and is a single piece.
|
In a compound
leaf the lamina is divided into smaller units called leaflets.
|
Ex.- Mango,
banana, banyan
|
Ex.- Rose, and
prickly poppy
|
(iii) Parallel
venation and reticulate venation.
Parallel
venation
|
Reticulate
venation
|
In this type of venation,
vein runs parallel to each other.
|
In this type of
venation, veins and veinlets are irregularly distributed in the lamina and
forms a network.
|
This appears in
monocot plants
|
This appears in
dicot plants
|
Ex.- Peepal,
mango, guava etc.
|
Ex.- banana,
grass, wheat etc
|
2.
What is the modification seen in Bryophyllum? Explain.
Bryophyllum is a plant whose leaves produce
adventitious buds in their
margin. The buds grow in to new plant when they fall
off from the
parent plant. It takes around 10 to12 days to grow
tiny plantlets out
from these buds.
3. What purpose
is served by the spines borne on the leaves of cactus?
Spines in the
cactus plants help in reducing the water loss.
4. Explain why
leaf survival is so important to the plant?
The survival of leaf is very important to the plant in
many ways, such as
a) Leaves prepare food and a part of this food is
needed by the plant
to survive. Photosynthesis is not possible without
leaves.
b) The transpiration process is not possible without
leaves. Hence
without leaves the transpiration pull will be affected
and the plants
cannot absorb more water and minerals from the soil.
This will affect
the growth of the plant.
5. Give an example of the following and
draw generalized diagram for
the same:
(i)
Simple leaf and compound leaf
(ii)
Parallel venation and reticulate venation.
(i) Simple
leaf: Example, Peepal Compound
leaf: example, Rose
(ii) Parallel
venation: Example, banana Reticulate
venation, Peepal
6.
Enlist some of the advantages of transpiration to green plants.
The advantage of transpiration to green plants are
Cooling effect: The water keeps on evaporating from the leaf surface
during transpiration. This helps the plant to cool
itself when it is hot
outside.
Transpirational pull: As water continuously evaporates from the
leaf
Surface, the roots pull up more water from the soil to
make up this water
Loss during the transpiration. As a result, important
mineral salts are also
Brought by the roots along with water from the soil.
These minerals help
the plant to grow.
7.
Why do some plants have to trap insects?
The soil in some areas are deficient in nitrates. So
the plants are not able
to get necessary nitrates from the soil. Some plants
develop their leaves
to trap insects to meet their nitrogen demand. These
plants utilizes the
insect’s protein by converting it in to nitrate. Some
example of such type
of plants are Pitcher plant, Venus flytrap and
Bladderwort.
8.
Explain some of the modifications of leaves found in plants.
Sometimes the complete leaf or a part of the leaf
modified to perform a
special function. Some of these modification are Leaf tendril, Spines and
Scale leaves.
Leaf tendril: In case of certain weak stemmed plants, the leaves or
leaflets are modified in to wiry, coiled structures.
These are called
tendrils. They are sensitive to touch. As they touch
any object they coil
around it and support the plant to climb up. Example:
Sweet pea.
Spines: Leaves are modified to spines to reduce water loss.
Example
cactus and prickly puppy
Scale leaves: Some plants like onion, ginger have thin and dry or
thick
and fleshy scale leaves. Their function is to protect
the buds.
9. What is tendril? Explain its use to the
plants.
In case of certain weak stemmed plants, the leaves or
leaflets are
modified in to wiry, coiled structures. These are
called tendrils. They
are sensitive to touch. As they touch any object they
coil around it
and support the plant to climb up. Example: Sweet pea.
******************************************************
Extra
Questions and Answers
A. Objective
Questions
1. Fill in the blanks:
a) The underground part of the plant is called root system.
b) The part of the plant which grows above the soil is
called shoot system.
c) Tap root system has a thick main root known as primary root.
d) The part of the stem between two successive nodes
is called internode.
e) Buds in the top of the shoot is called apical buds
f) Apical buds are
responsible for the vertical growth of the stem.
g) The angle between the upper side of the leaf and
the stem is known as
the axil.
h) Buds found in the axil are called the axillary buds.
i) The basal part of the leaf is petiole.
J) Leaves directly attached to the stem without a
petiole is called sessile
leaves.
k) The green flat and board part of the leaf is called
lamina.
l) Petiole continues to the lamina as the midrib.
m) Veins
provide a skeleton or supportive framework to the leaves.
n) During photosynthesis water is combined with carbon
dioxide to
produce glucose and
oxygen.
o) Plants which trap insects to meet their nitrogen
demand are called
insectivorous plant.
p) Leaves of Bryophyllum
and Begonia produces buds along
their margin.
q) Size of the pitcher varies from 10-20 cm.
r) At the bottom of the pitcher, enzymatic juices are
secreted.
s) Pitcher plants found in Garo
and Khasi hills in Meghalaya.
2. Give one word for the following.
a) The outer age of leaf – Margin.
b) The flat and green part of the shoot, that grows
laterally from the
nodes of the stem are called – Leaves.
c) The arrangement of leaves on a stem is called – Phyllotaxy.
d) Young tiny plants – Plantlets.
e) plant that bears buds in leaves for propagation – Bryophyllum.
B. Short Questions And Answers.
Define the following
a) Autotrophic nutrition: All
green plants prepare their own food. They
themselves prepare the nutrition for their use. This
method of nutrition is
called autotrophic nutrition.
b) Vegetative propagation:
Some new plants can be produced from the
vegetative parts of the plant such as roots, stems and
leaves. This type
of reproduction is called vegetative propagation.
c) Bladderwort:
Bladderwort has highly segmented leaves. Some of the
segments of these leaves form small bladder like
structures. The bladder
has an entry point which can be closed. The insects
enter in to it but
cannot come out and are digested inside.
d) The shoot system: The
part of the plant which grows above the soil is
called the shoot system. It is made up of Stem, Buds,
Leaves, Flowers
and Fruits.
C. Long Questions And Answers.
Answer the following:
1. What are the functions of stem?
The functions of stem are
a) Stem bears all aerial parts of the plant, buds,
leaves, flowers and
fruits.
b) Stem helps in the upward movement of water and
minerals absorb
by the root and transport them up to the leaves,
flowers and fruits.
c) Food prepared by the leaves is conducted downwards
to the roots
and other non-green parts by the stem.
d) Stem also manufactures food when green and young.
2. Mention the types of leave on the
basis of shape with example.
On the basis of shape the leaves are classified as
i) Needle shaped, e.g, pine, onion
ii) Oval, e.g, guava, apple
iii) Heart shaped, e.g, Peepal
iv) Oblong, e.g, banana
v) Circular, e.g, lotus, nasturtium
vi) Tapering, e.g, eucalyptus, ashoka
3. Mention the types of
leave on the basis of margin with example.
On the basis of margin the leaves are classified as
i) Complete or entire margin, e.g, peepal
ii) Toothed or serrated margin, e.g, china rose, rose
iii) Wavy margin, e.g, ashoka, mango
iv) Spinous margin, e.g, prickly puppy
4. Describe the different types of
arrangement of leaves with example.
The different types of arrangement of leaves are Alternate arrangement,
Opposite arrangement, Whorled arrangement.
Alternate arrangement: In this type arrangement only one leaf
arises from
each node. The next leaf arises from the successive
node in opposite
direction. Example: mint, Peepal, china rose.
Opposite arrangement: In this type of arrangement two leaves
arise from
each node opposite to each other. Example: guava and
jasmine.
Whorled arrangement: In this arrangement more than two leaves
are
attached in each node. Example: oleander.
5. Draw the structure of a leaf and
describe its different parts.
A leaf has three main parts. Petiole,
Lamina or leaf blade and Midrib.
Petiole: This is the basal part of the leaf. It
is attached to the stem at the node.
Leaf blade or lamina: The green, flat and
broad part of the leaf is known as lamina
or leaf blade. The outer age of leaf
blade is called leaf margin.
Midrib: Petiole continues to the lamina as
midrib. This laterally gives out fine branches called
veins. Petiole, midrib
and veins conduct water and food.
****************************************************




It is so much useful for me in this lockdown
ReplyDeleteThis is really very useful..
ReplyDeleteSupper
ReplyDeleteKg Wjemevexrgr
ReplyDeleteHelpful for me .
ReplyDeleteVERY NICE
ReplyDeleteFOR ME TOO
DeleteIt's good. Very helpful 👍👌
DeleteIt's very nice 👍☺️💕 It is really helpful 😊🙂😃 I like it very much!!
ReplyDeleteQuite helpful
ReplyDeleteICSE solution Sara book kitab mobile mein hai chapter mein hai vah Sara Sara Diya hun
ReplyDeleteYES
ReplyDeleteGreat Blog I Have Read Your Blog It Is Very Useful For Me Thank you for posting and sharing such great information.can you help me in finding out more about Basic Photosynthesis System Definition.
ReplyDeleteThanks very helpful
ReplyDeleteIt was helpful
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteLovely! I did not use it as I prefer doing it, in my own words but good efforts.... I am also a blogge- pls follow me- https://impactfulblogs.blogspot.com/
ReplyDeleteIt's is very nice 👍😊💕it is very helpfull
ReplyDelete